Use the following ChemTeX codes when editing or creating chemical formula or expression answers. ChemTeX is a subset of TeX. While some variations on the codes below may work, use these basic codes to optimize the performance of your content.
![]() To enter ChemTeX for chemical expressions in the Simple Editor
To enter ChemTeX for chemical expressions in the Simple Editor
Sample ChemTeX answer strings with rendered forms
| Answer attribute | Examples | ChemTeX code |
|---|---|---|
| Dot |
|
\cdot |
| Fraction |
|
\frac {top}{bottom} |
| Reaction symbols | ||
| Forward reaction |
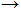
|
\rightarrow |
| Equilibrium reaction |
|
\rightleftharpoons |
| Stacked super/subscript isotope notation |
|
{^{super}_{sub}} or Single-digit super/subscripts do not need to be enclosed in a set of {}. |
| Subscript |
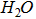
|
_{sub} or _s Single-digit subscripts do not need to be enclosed in a set of {}. |
| Superscripts | ||
| Pre-superscript only (isotope notation) |
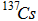
|
{^{super}} or {^s} The entire superscript expression must be enclosed in {}. Single-digit superscripts do not need to be enclosed in an extra set of {}. |
| Ion notation |
Single atoms, like: Molecules, like: |
{^{super}} or {^s} The entire superscript expression must be enclosed in {}. Single-digit superscripts do not need to be enclosed in an extra set of {}. |
|
Molecules ending with a subscript, like:
|
{molecule ending with a subscript}{^{super}} A molecular formula that ends with multiple atoms of an element must be enclosed in {} before attaching the charge as a post-superscript. |
|
| Symbols and variables | ||
| Antineutrino |
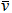 e and e and 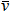 |
\bar{\nu}_{e} or \bar{\nu} |
| Energy | energy, Energy, ENERGY | energy, Energy, ENERGY (not case- sensitive) |
| Equations of state | (s), (l), (aq), and (g) |
(s), (l), (aq), and (g) s = solid, l ("ell") = liquid, aq = aqueous, and g = gas |
| Excited nuclei |
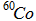 * *
|
{^\ast} or {^*} |
| Heat | heat, Heat, HEAT | heat, Heat, HEAT (not case-sensitive) |
| Lowercase Greek |
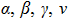
|
\alpha, \beta, \gamma, and \nu |
| No reaction | noreaction, Noreaction, NOREACTION |
noreaction, Noreaction, NOREACTION (not case-sensitive) Use for questions that ask students to predict a product formed when there is no reaction. When no reaction is used, it must be the complete answer. |
| Placeholders |
Elements: |
A, B, C, D, X, Y, and Z |
|
Lone pair of electrons: |
E | |
General ligand: 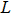 |
L | |
Generic metal: 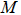 |
M | |
Arbitrary metal or metal ion: 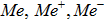 |
Me, Me{^+} or Me{^-} | |
Organic functional group: 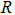 |
R | |
Arbitrary radical: 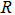 |
R | |