Use keyboard shortcuts
When you are answering questions in a player, you can cut, copy, and paste using the keyboard. You also can use keyboard shortcuts to enter special characters and symbols. For example, if you enter:
\sqrt
the square root symbol appears:
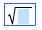
Math courses also include a palette of symbols where you can enter the special characters by clicking an icon on the palette. See Use the math palette for details on entering special characters and symbols from the palette in math courses.
Keyboard shortcuts are listed in the following tables:
Copy and paste shortcuts
To copy text:
- Highlight the text you want to copy.
- Press and hold down the Control key.
- Press the c key
- Release both keys.
To cut text:
- Highlight the text you want to cut.
- Press and hold down the Control key.
- Press the x key
- Release both keys.
To paste copied or cut text:
- Place your cursor where you want to paste the text.
- Press and hold down the Control key.
- Press the v key.
- Release both keys.
Common operation symbols
| To use this symbol... | Enter this shortcut... | For example |
|---|---|---|
| + (plus) | Plus sign on keyboard |
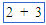
|
| - (minus) | Dash on keyboard |
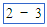
|
| = (equal) | Equal sign on keyboard |

|
 (multiplication dot) (multiplication dot) |
* (asterisk) (For example: 2 * 3) |
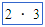
|
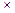 (times sign) (times sign) |
\times (For example: 2 \times 3) |
|
 (divided by) (divided by) |
\divide |
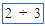
|
| < (less than) |
Left angle sign on keyboard (For example: 2 < 3) |

|
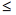 (less than or equal to) (less than or equal to) |
< = (left angle sign and an equal sign) (For example: 2 <= 3) |

|
| < (greater than) |
Right angle sign on keyboard (For example: 3 > 2) |

|
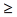 (greater than or equal to) (greater than or equal to) |
> = (right angle sign and an equal sign) (For example: 3 >= 2) |
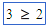
|
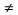 (not equal) (not equal) |
<> (left and right angle signs) (For example: 3 <> 2) |

|
Math function symbols
| To use this symbol... | Enter this shortcut... | For example |
|---|---|---|
 (fraction) (fraction) |
/ (Type the numerator, then a slash, then the denominator. For example: 2 /3) |
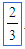
|
 (superscript) (superscript) |
Shift (Type the Shift key, then the up arrow ( |

|
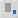 (subscript) (subscript) |
Shift (Type the Shift key, then the down arrow ( |
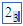
|
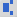 (superscript and subscript) (superscript and subscript) |
\supsub (Creates a template where you can enter the base value in the box on the left, and the superscript and subscript in the boxes on the right.) |
|
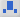 (double subscripts) (double subscripts) |
\subsub (Creates a template where you can enter a subscript in the box on the left, the base value in the box in the middle, and a subscript in the box on the right.) |
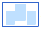 (empty template) (empty template)
|
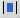 (absolute value) (absolute value) |
\abs (Creates a template where you can enter a value in the blue box.) |
|
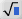 (square root) (square root) |
\sqrt (Creates a template where you can enter a value in the blue box.) |
|
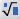 (Nth-root) (Nth-root) |
\nrt (Creates a template where you can enter the values in the blue boxes.) |
|
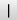 (vertical bar) (vertical bar) |
\textbar (For example: 5 \textbar 15) |

|
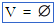
 (empty set) (empty set) |
\empty (For example: V = \empty) |
|
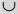 (union) (union) |
\cup (For example: A \cup B) |
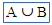
|
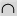 (intersection) (intersection) |
\cap (For example: A \cap B) |
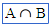
|
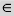 (element of) (element of) |
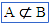
\element (For example: A \element B) |
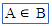
|
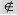 (not an element of) (not an element of) |
\nelement (For example: A \nelement B) |
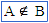
|
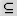 (subset of) (subset of) |
\subset (For example: A \subset B) |
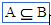
|
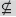 (not a subset of) (not a subset of) |
\nsubset (For example: A \nsubset B) |
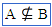
|
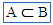
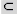 (proper subset of) (proper subset of) |
\propersub (For example: A \propersub B) |
|
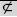 (not a proper subset of) (not a proper subset of) |
\npropersub (For example: A \npropersub B) |
|
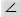 (angle) (angle) |
\angle (For example: \angle ABC) |

|
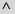 (logical and) (logical and) |
\and (For example: A \and B) |
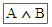
|
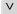 (logical or) (logical or) |
\or (For example: A \or B) |
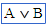
|
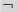 (logical not) (logical not) |
\not (For example: \not A) |
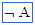
|
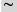 (equivalent) (equivalent) |
Tilde on keyboard |
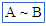
|
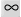 (infinity) (infinity) |
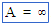
\inf (For example: A = \inf) |
|
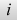 (imaginary unit) (imaginary unit) |
i on keyboard (For example: a = bi = 0) |
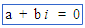
|
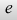 (Euler's number) (Euler's number) |
e on keyboard (For example: e = 0) |
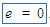
|
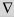 (gradient) (gradient) |
\grad (For example: \grad f = 2y) |
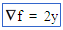
|
 (integral) (integral) |
\int (For example: \int f(x) dx |

|
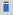 (over-bar) (over-bar) |
\bar (Creates a template where you can enter a value in the blue box.) |
|
 (double overbar) (double overbar) |
\dbar (Creates a template where you can enter a value in the blue box.) |
|
 (hat) (hat) |
\hat (Creates a template where you can enter a value in the blue box.) |
|
Greek letters
| To use this letter... .. | Enter this shortcut... .. |
|---|---|
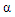 lower-case alpha lower-case alpha |
\alpha |
|
|
\beta |
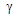 lower-case gamma lower-case gamma |
\gamma |
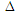 upper-case delta upper-case delta |
\cdelta |
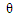 lower-case theta lower-case theta |
\theta |
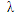 lower-case lambda lower-case lambda |
\lambda |
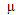 lower-case mu lower-case mu |
\mu |
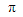 lower-case pi lower-case pi |
\pi |
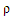 lower-case rho lower-case rho |
\rho |
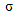 lower-case sigma lower-case sigma |
\sigma |
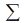 upper-case sigma upper-case sigma |
\sum |
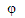 lower-case phi lower-case phi |
\phi |
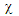 lower-case chi lower-case chi |
\chi |
See also:
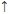 ) to create a superscript box where you can enter a number.)
) to create a superscript box where you can enter a number.)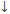
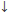 ) to create a subscript box where you can enter a number.)
) to create a subscript box where you can enter a number.)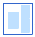 (empty template)
(empty template)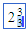 (template with values)
(template with values)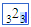 (template with values)
(template with values)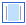 (empty template)
(empty template)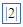 (template with value)
(template with value)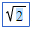 (template with value)
(template with value)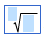 (empty template)
(empty template) 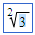 (template with values)
(template with values) (empty template)
(empty template) (template with value)
(template with value) (empty template)
(empty template) (template with value)
(template with value) (empty template)
(empty template)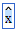 (template with value)
(template with value)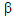 lower-case beta
lower-case beta